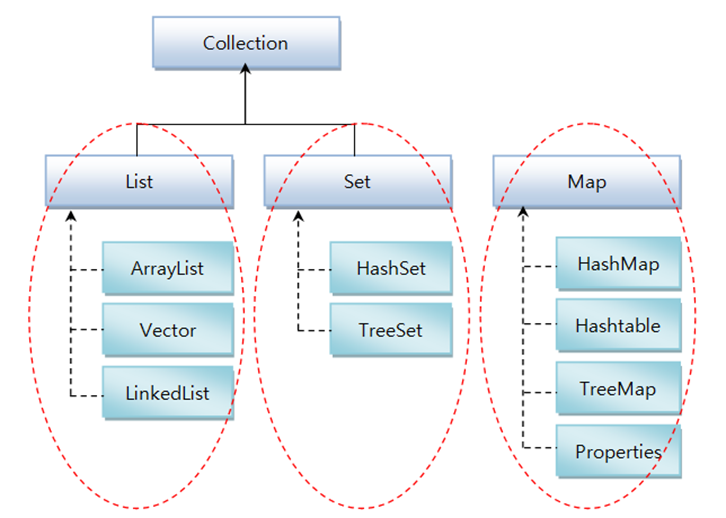
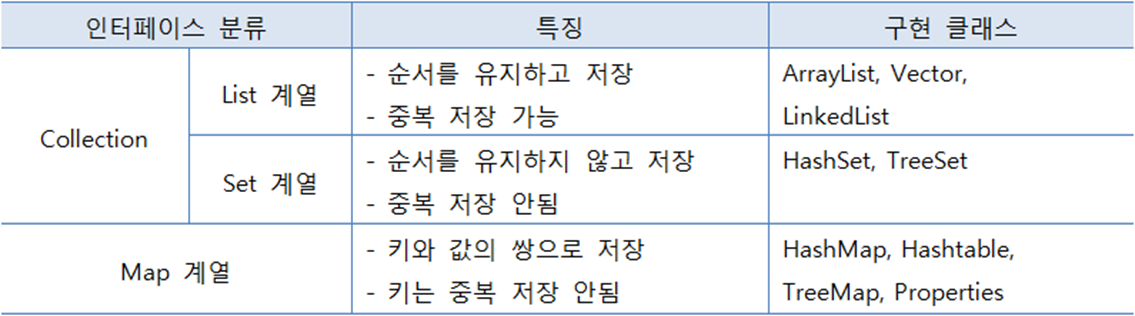
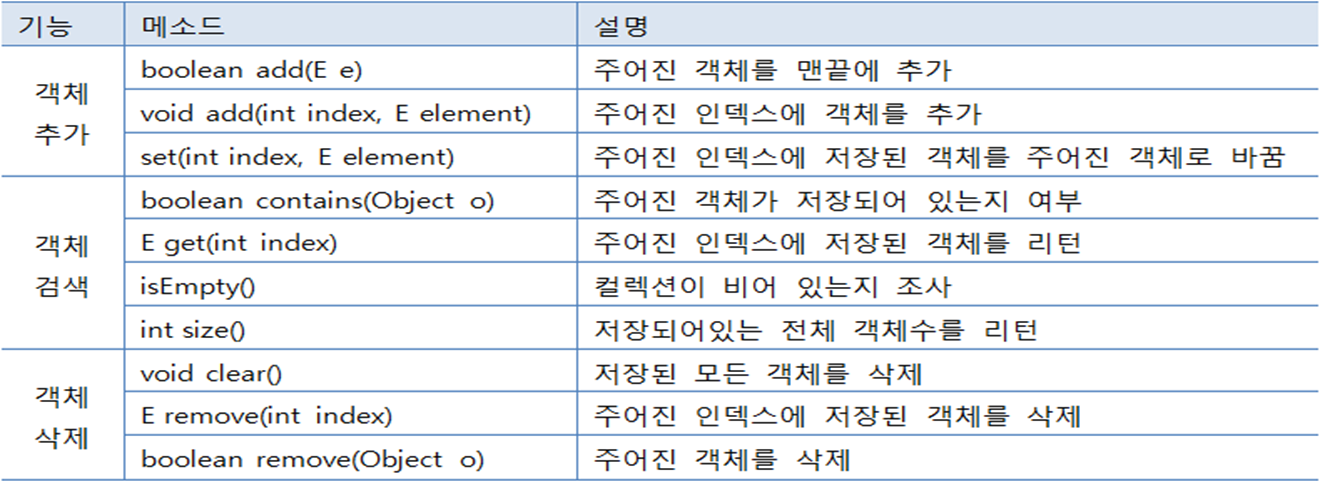
ArrayList , HashMap 자주 쓰임
List 컬렉션의 특징 및 주요 메소드
package c1_list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 순서(index)가 존재하고 데이터 중복저장이 가능한 List
// java.util.*
ArrayList array = new ArrayList();
array.add("문자열");
array.add(100);
// get(index) : 값 꺼내옴
// 제네릭 타입지정 안하면 Object타입임
String str = (String)array.get(0);
ArrayList<String> strs = new ArrayList<>();
strs.add("java");
strs.add("JDBC");
strs.add(null);
// list에 삽입된 항목의 크기
int size = strs.size();
System.out.println("size : " + size);
strs.add("MySQL");
strs.add("mysql");
size = strs.size();
System.out.println("size : " + size);
String result = strs.toString();
System.out.println(result);
String str2 = strs.get(0);
System.out.println(str2);
// size() : 실제 들어간 항목의 크기
for(int i = 0; i < strs.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(strs.get(i));
}
System.out.println("===================");
for(String s : strs) {
System.out.println(s);
}
strs.add(2,"Servlet/JSP");
System.out.println(strs);
strs.set(3, "Spring");
System.out.println(strs);
// [java, JDBC, Servlet/JSP, Spring, MySQL, mysql]
// 삭제
boolean isChecked = strs.remove("JDBC");
System.out.println("isChecked : "+isChecked);
System.out.println(strs);
result = strs.remove(2);
System.out.println("삭제한 항목 : " + result);
System.out.println(strs);
// 값의 존재 확인
// 리스트에 매개변수로 전달받은 값과 일치하는 값이 존재하면 true, 없으면 false
isChecked = strs.contains("mysql");
System.out.println("isChecked : " + isChecked );
// 저장된 항목이 존재하지 않으면 true, 저장된 값이 존재하면 false
isChecked = strs.isEmpty();
System.out.println("isChecked : " + isChecked );
// 리스트에 저장된 모든 항목을 제거
strs.clear();
System.out.println(strs.size());
System.out.println("isEmpty : " + strs.isEmpty());
}
}
package c1_list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
class Board{
String subject;
String content;
String writer;
// alt + s + a
public Board(String subject, String content, String writer) {
this.subject = subject;
this.content = content;
this.writer = writer;
}
}
public class LinkedListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Board> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Board> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
// 추가 - 검색 작업 진행 시간 체크
long startTime = 0;
long endTime = 0;
int size = 100000;
System.out.println("[ 추가 작업 ]");
startTime = System.nanoTime();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
arrayList.add(0, new Board("제목"+i,"내용"+i,"작성자"+i));
}
endTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.printf("array 추가시간 %d ns %n",(endTime-startTime));
startTime = System.nanoTime();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
linkedList.add(0, new Board("제목"+i,"내용"+i,"작성자"+i));
}
endTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.printf("linked 추가시간 %d ns %n",(endTime-startTime));
System.out.println("[ 검색 작업 ]");
startTime = System.nanoTime();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
arrayList.get(i);
}
endTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("array 검색시간 : " + (endTime-startTime) +"ns");
startTime = System.nanoTime();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
linkedList.get(i);
}
endTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("linked 검색시간 : " + (endTime-startTime) +"ns");
}
}
Set 컬렉션의 특징 및 주요 메소드
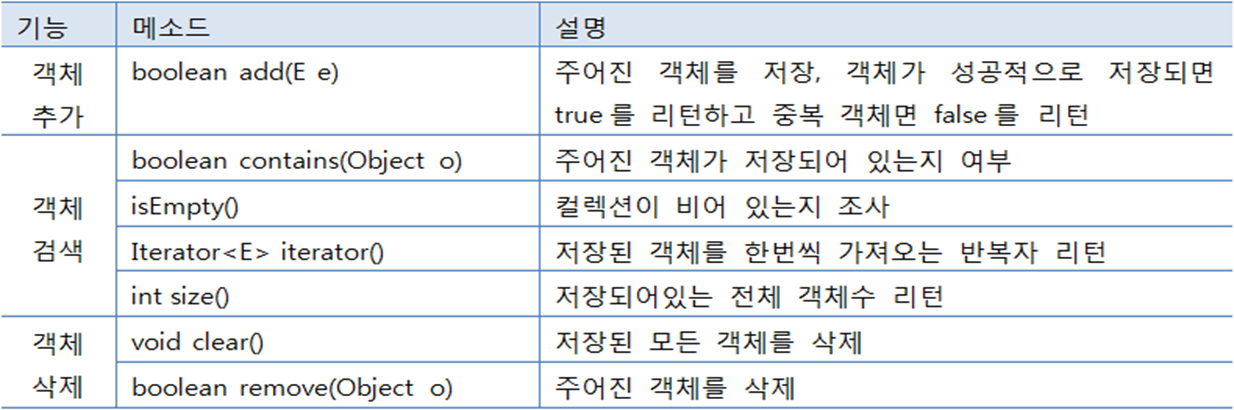
특징
동일 객체 및 동등 객체는 중복 저장하지 않음
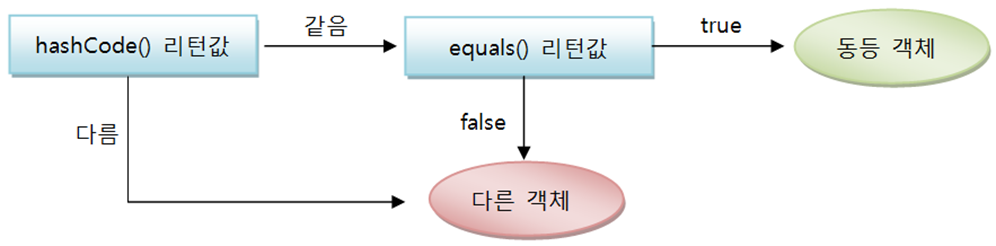
동등 객체 판단 방법
Iterator로 검색가능, 삭제 가능
package c2_set;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashSetExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> s1 = new HashSet<>();
s1.add("A");
s1.add("D");
s1.add("B");
s1.add("C");
System.out.println(s1);
boolean isAdd = s1.add("C");
System.out.println("isAdd : " + isAdd );
System.out.println(s1.size());
// 반복자
// java.util.*
Iterator<String> itr = s1.iterator();
//.hasNext() : 내부에 꺼내올 값이 존재하냐?
while(itr.hasNext()) {
String s = itr.next();
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(s1.contains("B"));
Set<String> s2 = new HashSet<>();
s2.add("A");
s2.add("D");
s2.add("E");
System.out.println(s2);
// s2 : [A, D, E]
// s3 : [A, B, C, D]
// s1 set을 복제한 새로운 Set instance 생성
Set<String> s3 = new HashSet<>(s1);
System.out.println(s3);
// 합집합
s3.addAll(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
Set<String> s4 = new HashSet<>(s1);
System.out.println("s4: " + s4);
System.out.println("s2: " + s2);
// 교집합
boolean isOk = s4.retainAll(s2);
System.out.println("is Ok : " + isOk);
for(String s : s4) {
System.out.print(s + " ");
//반복문 안에서 삭제하면 오류남.(순회하는 중 크기달라져서)
if(s.equals("A")) {
// s4.remove(s);
}
}
System.out.println();
// 순회하면서 삭제하는 방법 (List도 마찬가지)
Iterator<String> itr2 = s4.iterator();
while(itr2.hasNext()) {
String s = itr2.next();
if(s.equals("A")) { // iterator위치가 "A"일때
itr2.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(s4);
s1.add(null);
s1.add("안녕");
s1.add(null); //중복불가
System.out.println(s1);
}
}
package c2_set;
public class Member {
private int num;
private String name;
private int age;
// 생성자
public Member(int num, String name, int age) {
super();
this.num = num;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 앞에 hash붙어있으면 비교시 hashcode,equals비교함. -> hashcode재정의(필드값이용),equals재정의
// hashcode 같으면 equals 수행
@Override
public int hashCode() {
System.out.println("hashCode 호출" + super.hashCode());
return this.num + this.age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
System.out.println("equals 호출");
if(obj instanceof Member) {
Member m = (Member)obj;
if(m.name.equals(this.name)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
package c2_set;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashCodeExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name1 = "최기근";
String name2 = "최기근";
String name3 = new String("최기근");
//String 문자열이 같으면 동일한 hashCode반환
System.out.println(name1.hashCode());
System.out.println(name2.hashCode());
System.out.println(name3.hashCode());
Member member1 = new Member(1,name1,20);
Member member2 = new Member(2,name2,22);
Member member3 = new Member(1,name3,20);
// ctrl + shift + o
Set<Member> setMember = new HashSet<>();
setMember.add(member1);
System.out.println(member1.hashCode());
setMember.add(member2);
System.out.println(member2.hashCode());
setMember.add(member3);
System.out.println(member3.hashCode());
System.out.println(setMember.size());
System.out.println(setMember);
}
}
Map 컬렉션의 특징 및 주요 메소드
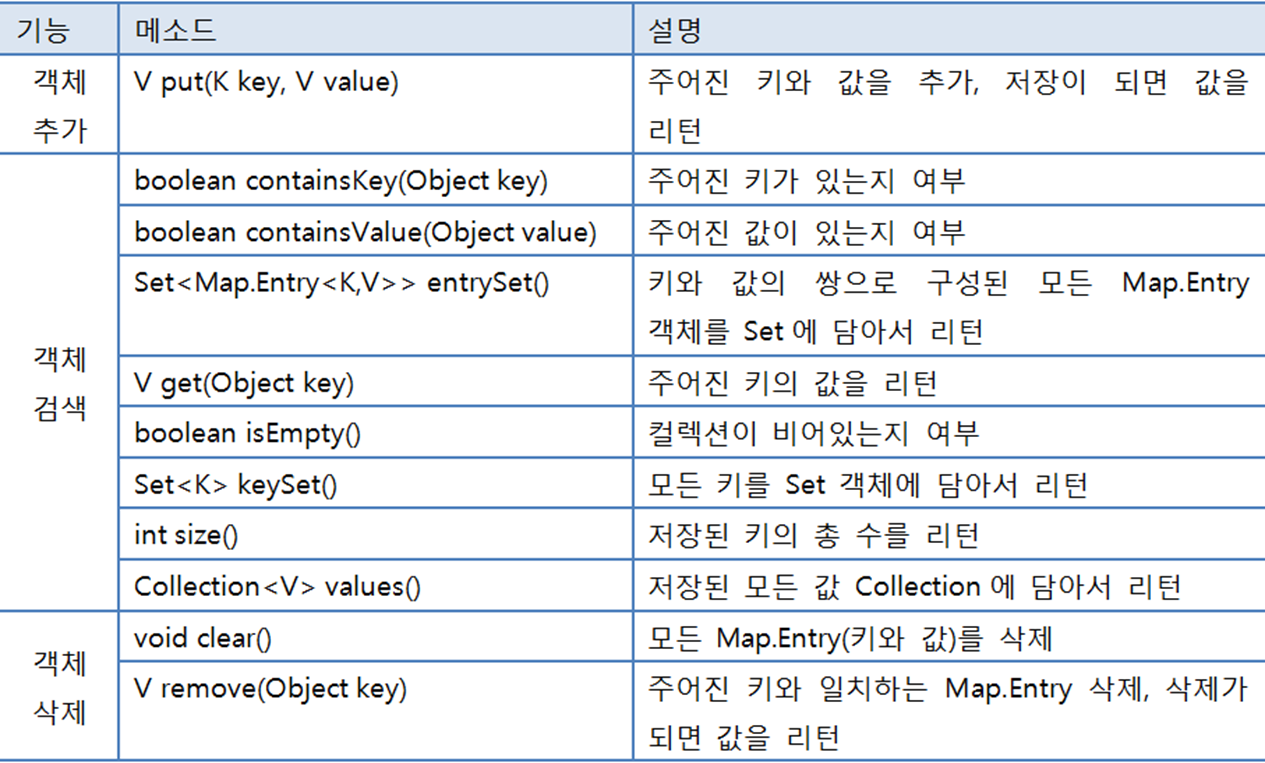
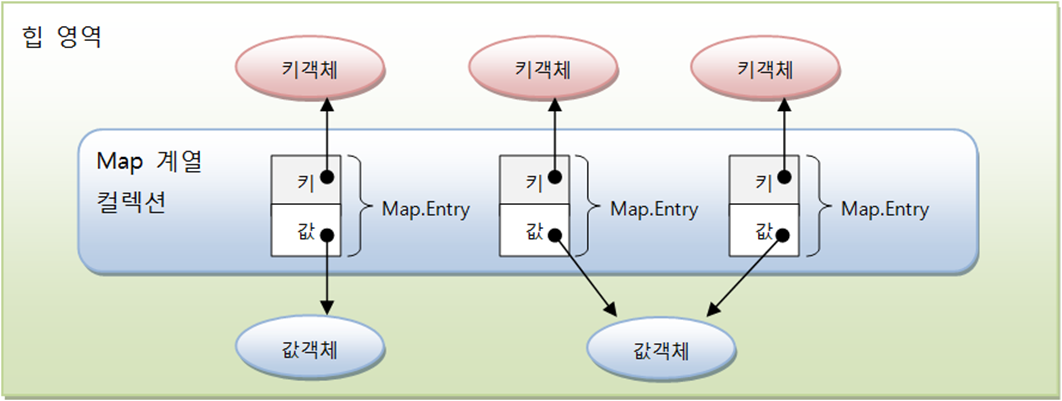
키값은 set에 따로 저장. entry추가할때 키 중복시 value 값 덮어쓰기함.

package c3_map;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashMapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("최기근", 100);
map.put("이수석", 60);
map.put("이진형", 90);
map.put("김선경", 80);
System.out.println(map); // 무작위 나열
// 저장된 순서를 기억하는 map
Map<String,Integer> linkedMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
linkedMap.put("최기근", 100);
linkedMap.put("이수석", 60);
linkedMap.put("이진형", 90);
linkedMap.put("김선경", 80);
System.out.println(linkedMap);// 삽입한 순서대로 나열
// map에 중복 키 삽입
map.put("이수석", 85);
System.out.println(map); // 새로운 값으로 교체됨
//key값이 일치하는 entry에 value값을 반환
int score = map.get("최기근");
System.out.println("최기근 점수 : " + score);
System.out.println(map.size());
// 동일한 key값을 가진 entry를 삭제
map.remove("김선경");
System.out.println(map.size());
System.out.println(map);
boolean isChecked = map.containsKey("이수석");
System.out.println("존재하는 key값인가 :" + isChecked);
// value에 100점이 존재하는가
isChecked = map.containsValue(100);
System.out.println("value 존재 :" + isChecked);
Set<Entry<String,Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
Iterator <Entry<String,Integer>> iterator = entrySet.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry = iterator.next();
String key = entry.getKey();
int value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("key: " +key + ", value : "+value );
}
//keySet , 맵에 저장된 entry의 key 묶음
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
Iterator<String> keyItr = keySet.iterator();
while(keyItr.hasNext()) {
String key = keyItr.next();
int value = map.get(key);
System.out.printf("%s=%d,",key,value);
}
System.out.println();
for(String s : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println("key : " +s);
}
// map에 저장된 value값을 나열(value값은 중복가능이니까 collection에 집어넣음)
Collection<Integer> values = map.values();
int sum = 0;
for(int value : values) {
System.out.print(value + ", ");
sum+= value;
}
System.out.println("sum : " + sum);
System.out.println("평균 : "+(sum/map.size()));
}
}
Properties
특징
키와 값을 String 타입으로 제한한 Map 컬렉션. 설정값 저장할 때 주로 사용
Properties는 프로퍼티(~.properties) 파일을 읽어 들일 때 주로 사용
package c3_map;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Properties;
//일반적으로 Properties는 설정정보를 저장하고 사용하는 파일.
public class PropertiesExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.put("key", "value");
prop.put("score", 10); //map 객체처럼 사용하는건 올바른 방식 아님.
System.out.println(prop);
prop.setProperty("key", "key value"); //put과 동일한 기능, 값은 문자열로 제한
System.out.println(prop);
String value = prop.getProperty("key");
System.out.println(value);
System.out.println("===================================");
Properties system = System.getProperties();
System.out.println(system);
System.out.println("============================");
// 경고
//getResource : 해당 클래스 위치에서 파일 찾아가는 함수
URL url = PropertiesExample.class.getResource("info.properties");
String path = url.getPath();//파일경로
System.out.println(path);
Properties prop2 = new Properties();
try {
//load : 엔트리형식으로 만들어줌
prop2.load(new FileReader(path));
System.out.println(prop2.getProperty("id"));
System.out.println(prop2.getProperty("pw"));
System.out.println(prop2.getProperty("name"));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package c4_tree; //이진트리구조
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class TreeSetExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Integer> treeSet = new TreeSet<>();
treeSet.add(87);
treeSet.add(75);
treeSet.add(90);
treeSet.add(80);
treeSet.add(80); // 중복 저장 불가능
System.out.println(treeSet.size());
System.out.println(treeSet); //값 입력시 정렬됨
Iterator<Integer> itr = treeSet.descendingIterator(); // 역순반복자도 있다.
while(itr.hasNext()) {
int i = itr.next();
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//역순으로 정렬
TreeSet<Integer> decendingSet
= (TreeSet<Integer>)treeSet.descendingSet();
System.out.println(decendingSet);
int score = 0;
// [75, 80, 87, 90] - treeSet
score = treeSet.first();
System.out.println("첫번째 값: " + score); //최소값
score = treeSet.last();
System.out.println("마지막 값: " + score); //최대값
score = treeSet.lower(87);
System.out.println("87보다 낮은 수(바로 아래) : "+score);
// 80
score = treeSet.higher(87);
System.out.println("87보다 높은 수(바로 위) : "+score);
// 90
score = treeSet.floor(85);
System.out.println("85이거나 그 아래 수 : " + score);
// 80
score = treeSet.ceiling(85);
System.out.println("85이거나 그 위의 수 : "+score);
//87
System.out.println(treeSet);
//값을 꺼내오는 것.
score = treeSet.pollFirst();
System.out.println("score : "+score);
System.out.println(treeSet);
score = treeSet.pollLast();
System.out.println("score : "+score);
System.out.println(treeSet);
// TreeMap : 키값 기준으로 정렬됨
TreeMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(100, "최기근");
map.put(15, "이순신");
map.put(89, "김유신");
map.put(97, "유관순");
System.out.println(map);
Entry<Integer,String> entry = null;
entry = map.firstEntry();
System.out.println("가장 낮은 entry : " + entry);
int key = map.firstKey();
System.out.println("가장 낮은 키 값 : " + key);
}
}
package c4_tree;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(100, "최기근");
map.put(15, "이순신");
map.put(89, "김유신");
map.put(97, "유관순");
System.out.println(map);
Map.Entry<Integer,String> entry = null;
entry = map.firstEntry();
System.out.println("가장 낮은 수 : " +entry.getKey()+" "+entry.getValue());
entry = map.lastEntry();
System.out.println("가장 높은 수 : " +entry.getKey()+" "+entry.getValue());
entry = map.higherEntry(90);
System.out.println("90보다 높 수 : " +entry.getKey()+" "+entry.getValue());
entry = map.lowerEntry(90);
System.out.println("90보다 낮은 수 : " +entry.getKey()+" "+entry.getValue());
entry = map.floorEntry(90);
System.out.println("90이거나 보다 낮은 수 : " +entry.getKey()+" "+entry.getValue());
entry = map.ceilingEntry(90);
System.out.println("90이거나 보다 높은 수 : " +entry.getKey()+" "+entry.getValue());
int i = map.firstKey();
System.out.println("첫번째 키값 : " + i);
i = map.lastKey();
System.out.println("마지막 키값 : " + i);
// ...
while(!map.isEmpty()) {
entry = map.pollFirstEntry();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() +" " + entry.getValue());
System.out.println("남은 객체 수 : " + map.size());
}
System.out.println(map);
}
}
package c5_stack_queue;
import java.util.Stack;
class Coin{
private int value;
public Coin(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return this.value;
}
}
public class StackExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// stack - LIFO(Last In First Out)
// 자료 구조를 구현할 class
Stack<Coin> coinBox = new Stack<>();
coinBox.push(new Coin(50));
coinBox.push(new Coin(100));
coinBox.push(new Coin(500));
coinBox.push(new Coin(100));
System.out.println(coinBox.size());
Coin coin = coinBox.peek();
System.out.println("value : " + coin.getValue());
System.out.println(coinBox.size());
coin = coinBox.pop();
System.out.println("소모된 동전 : "+coin.getValue());
System.out.println(coinBox.size());
System.out.println(coinBox.peek().getValue());
while(!coinBox.isEmpty()) {
coin = coinBox.pop();
System.out.println(coin.getValue()+"원");
System.out.println(coinBox.size());
}
}
}
Stack 클래스
특징
후입선출(LIFO: Last In First Out) 구조
응용 예: 브라우저 뒤로가기
Queue 인터페이스
특징
선입선출(FIFO: First In First Out)
응용 예: 작업 스케줄러
구현 클래스: LinkedList
package c5_stack_queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//FIFO - (First In First Out)
Queue<String> messageQueue = new LinkedList<>();
messageQueue.offer("아버지에게 안부 메세지");
messageQueue.offer("어머니에게 안부 메세지");
messageQueue.offer("이모에게 안부 메세지");
System.out.println(messageQueue.size());
String peekMessage = messageQueue.peek();
System.out.println("수행해야할 기능 : " + peekMessage);
while(!messageQueue.isEmpty()) {
String message = messageQueue.poll();
System.out.println("수행한 기능 :" + message);
System.out.println(messageQueue.size());
}
}
}
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 05.16. IO기반 입출력 (0) | 2023.05.16 |
|---|---|
| 05.12실습 (0) | 2023.05.12 |
| 05.10 Class복습,String클래스,정규표현식,Math클래스, (0) | 2023.05.10 |
| 05.09 예외처리 (0) | 2023.05.09 |
| 05.08 제네릭 와일드카드, Object, 예외처리 (0) | 2023.05.08 |
